Primary, secondary, tertiary
Daniel Fürth
Assistant professor
SciLifeLab/Uppsala University
🔗 furthlab.xyz
@furthlab
Course Syllabus: 🔗3MG022
Knowledge and understanding
“Explain current techniques for research, diagnostics and treatment of genetic diseases including cancer”
Competence and skills
“independently analyse, process and formulate relevant scientific questions…”
Judgement and approach
“…ability to critically evaluate and appraise scientific research…”
Topics covered today:
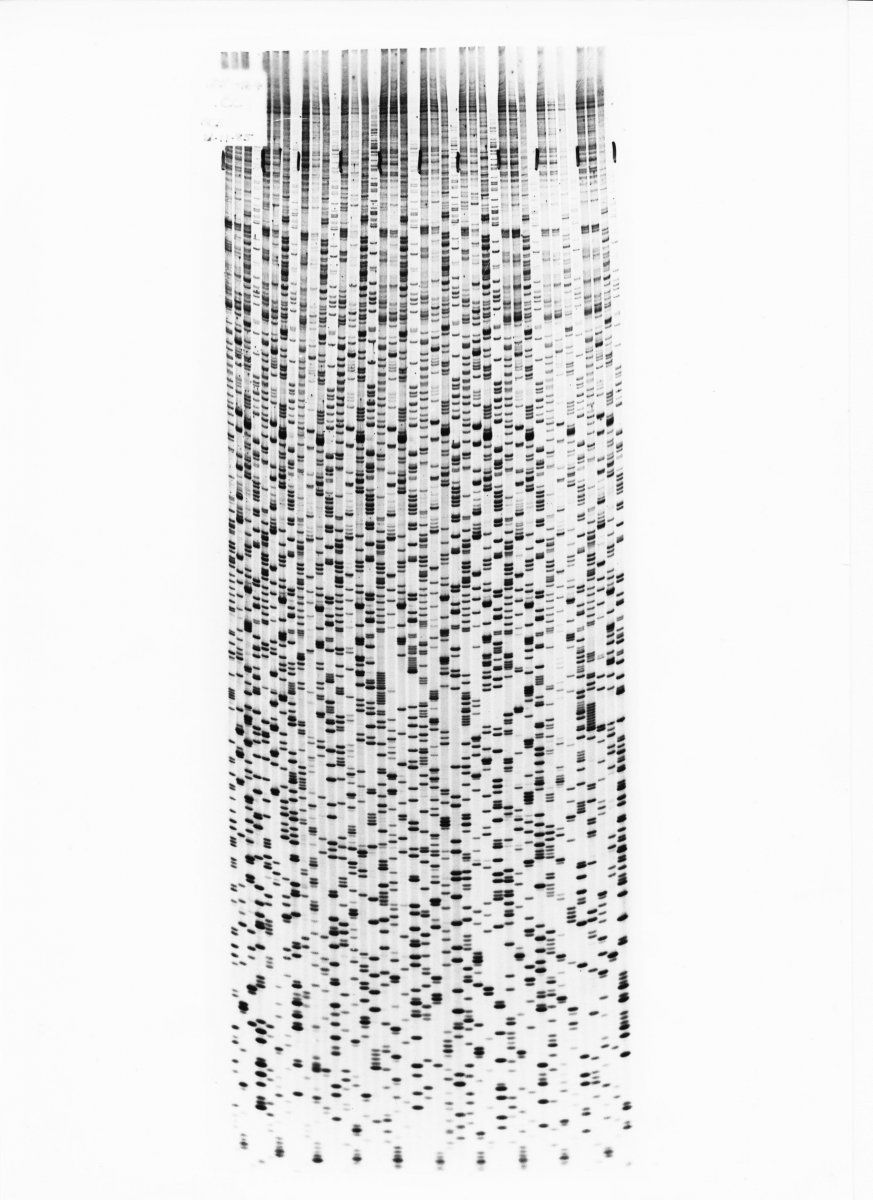
Electrophoretic machine as designed by Tiselius
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)
Molecules can be run in their “native state”
preserving higher-order structure.
Or a chemical denaturant can be added to
remove structure (urea for 🧬).
Native vs non-native PAGE.
Pore size controled by % of acrylamide.
📏 Resolution:
100-1000 nt down to single-nucleotide.
“structure of proteins, especially that of insulin”
“determination of base sequences in nucleic acids”

📜 Sanger sequencing ➡️ single-cell methods

The golden era ⚜️⚱️🏆 of molecular biology 🧬.
🇺🇸 Restriction and modification enzymes 🇨🇭
🏅Noble Prize: 🇺🇸 Hamilton O. Smith, 🇺🇸 Daniel Nathans, and 🇨🇭 Werner Arber.
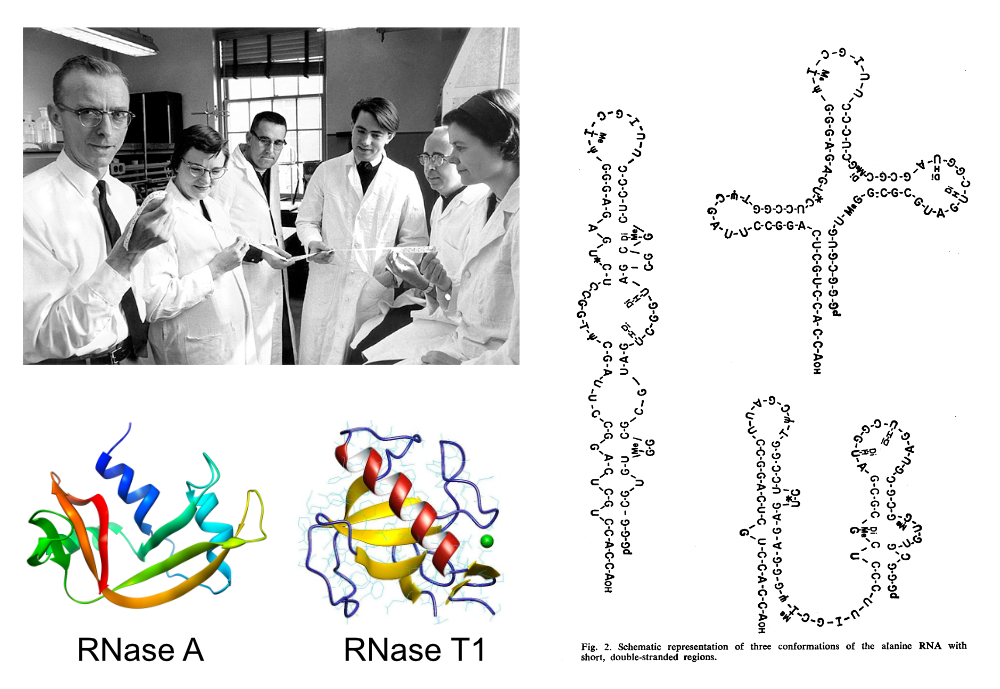
RNase A (Bovine pancreas ribonuclease):
RNase T1 (Taka-Diastase ribonuclease T1):
A proto sequencing method.
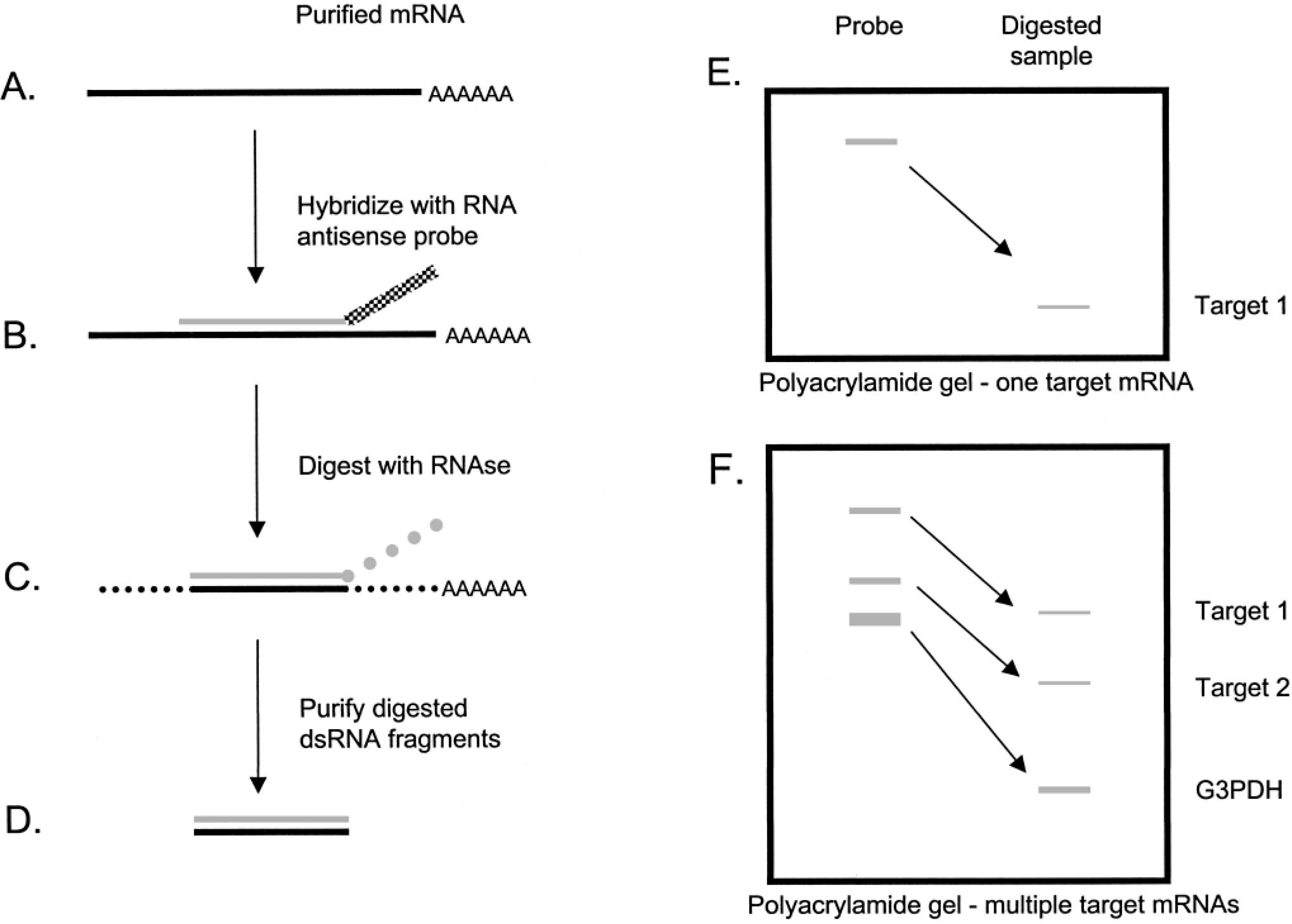
A proto sequencing method.
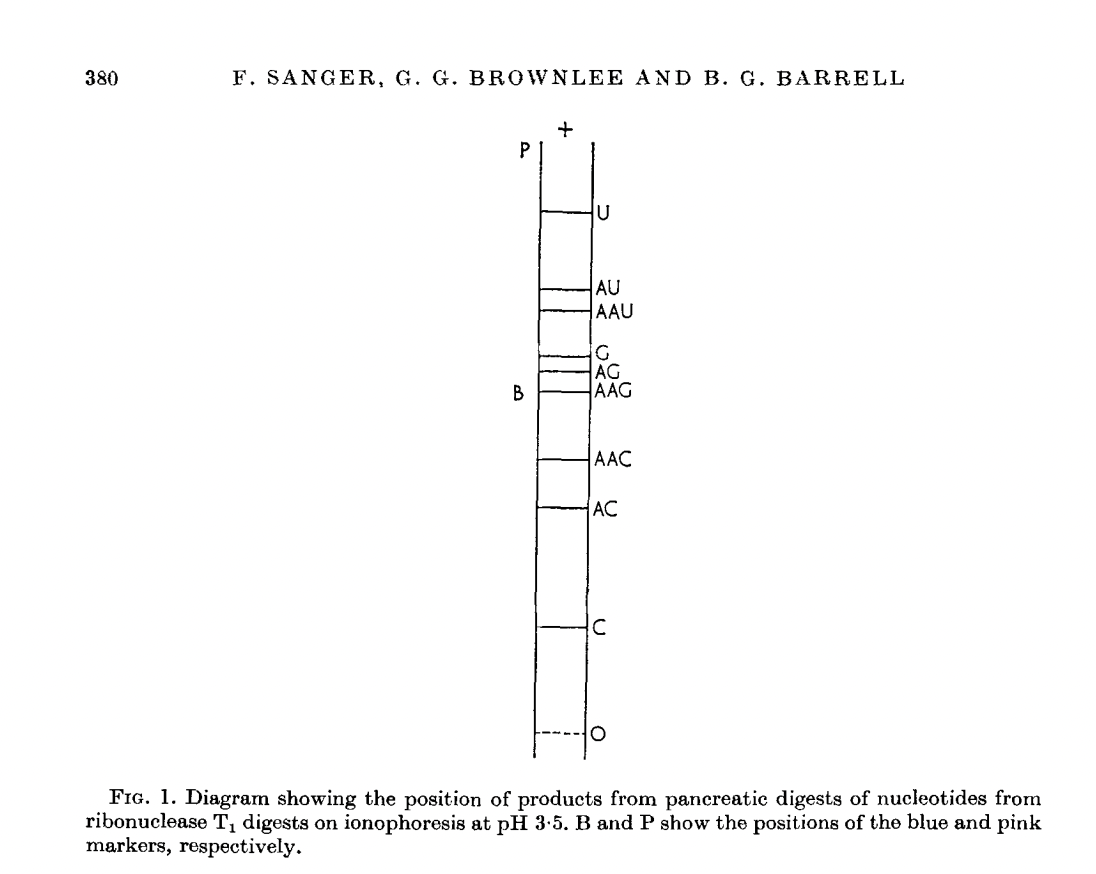
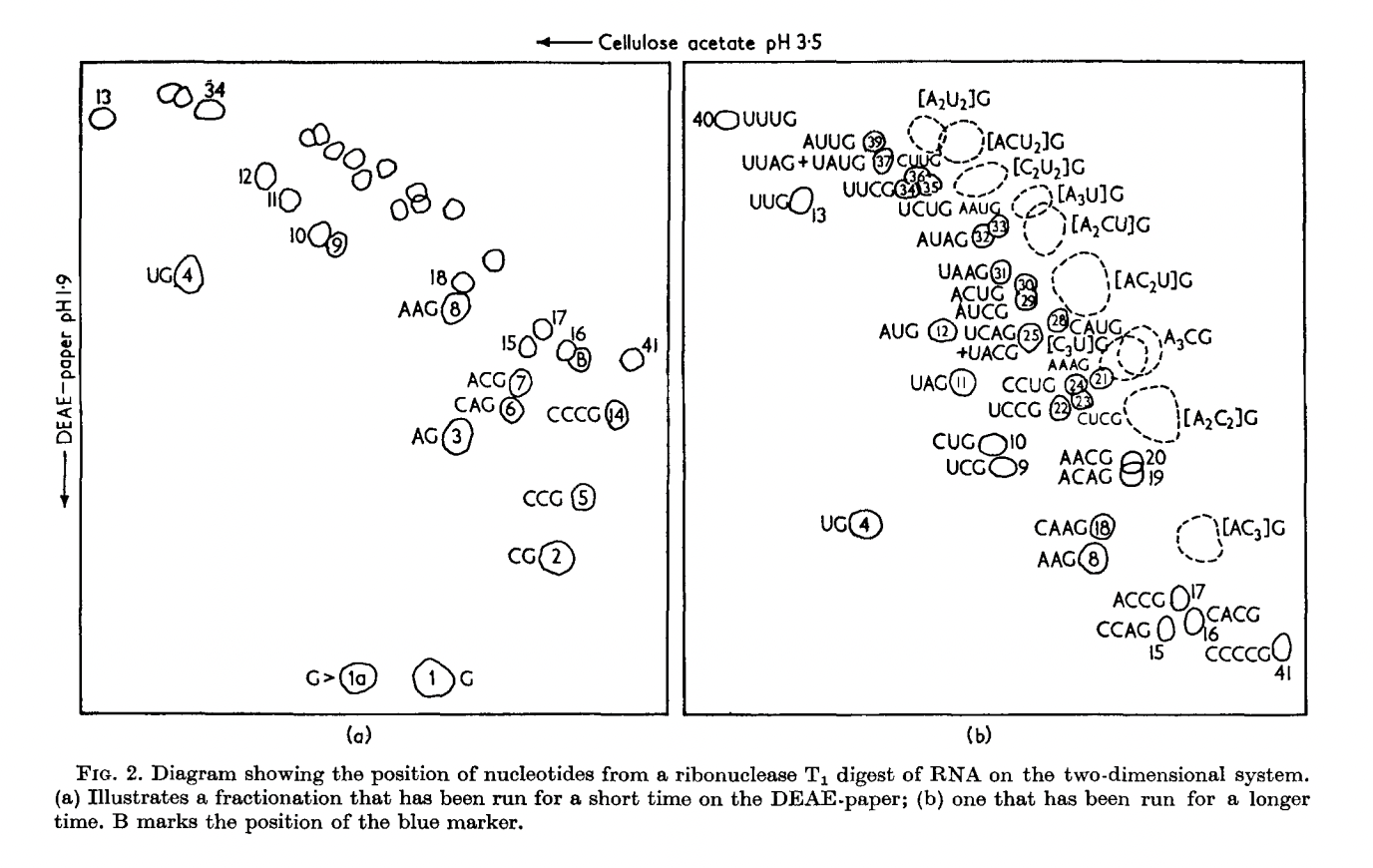
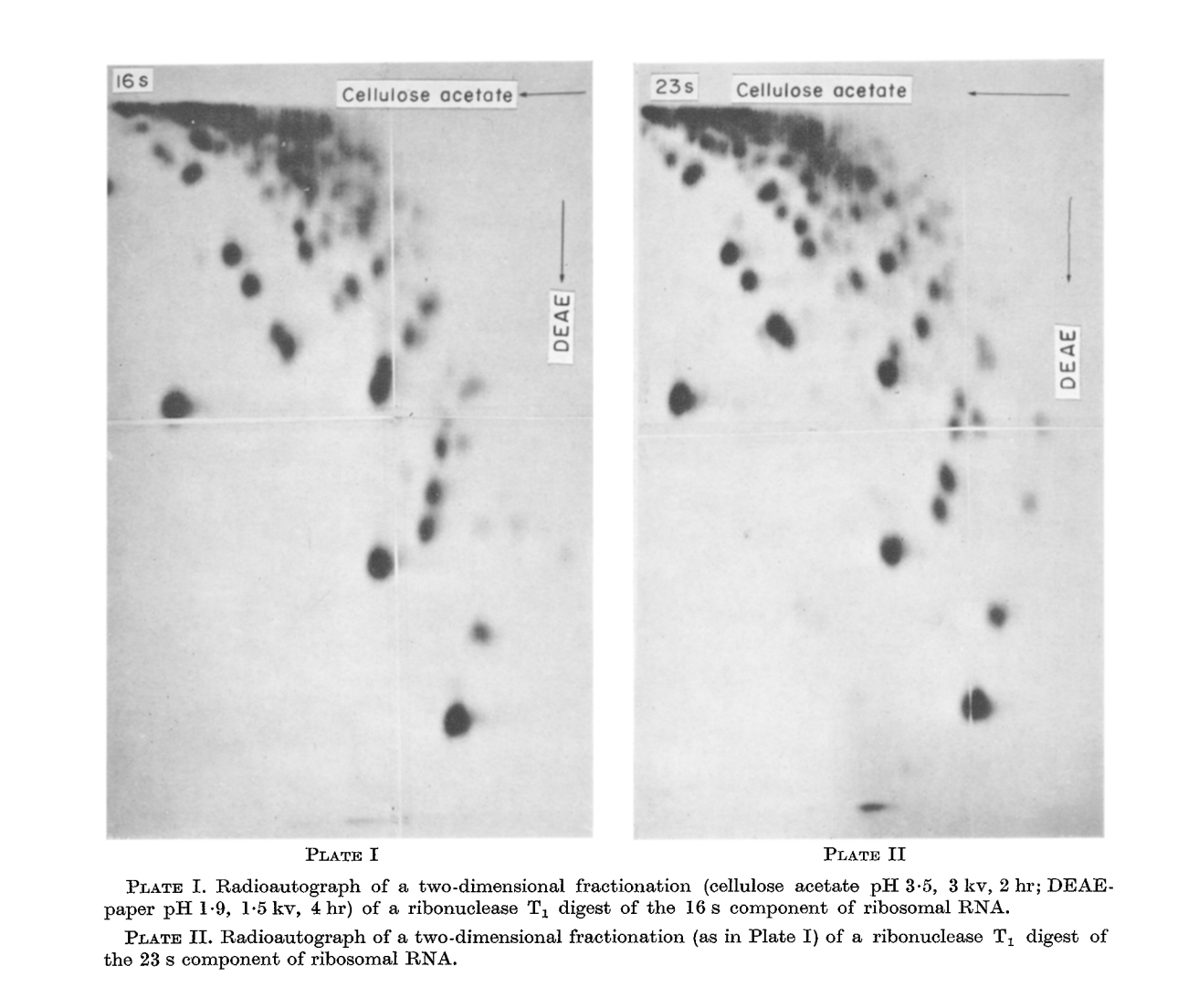
The birth of the “-”-approach of Sanger.

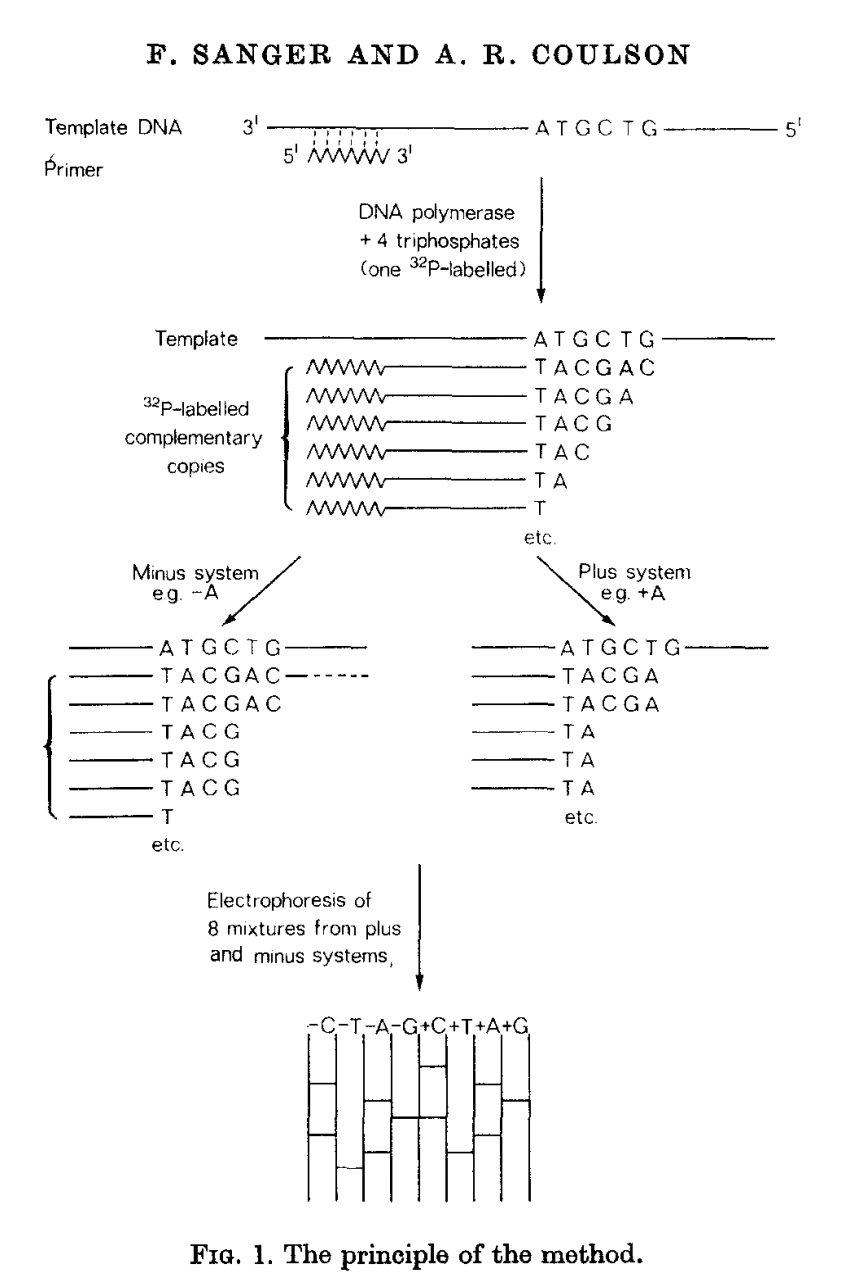
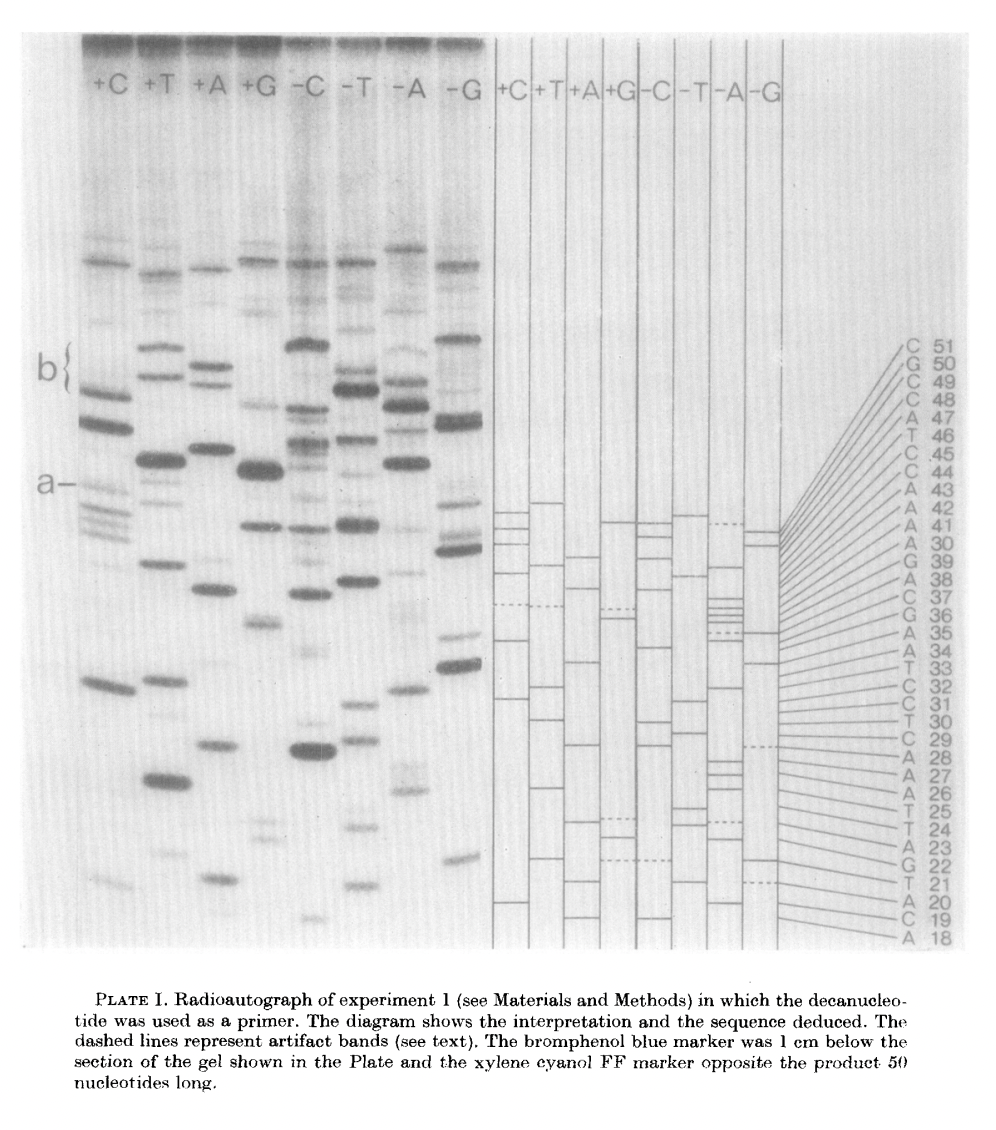
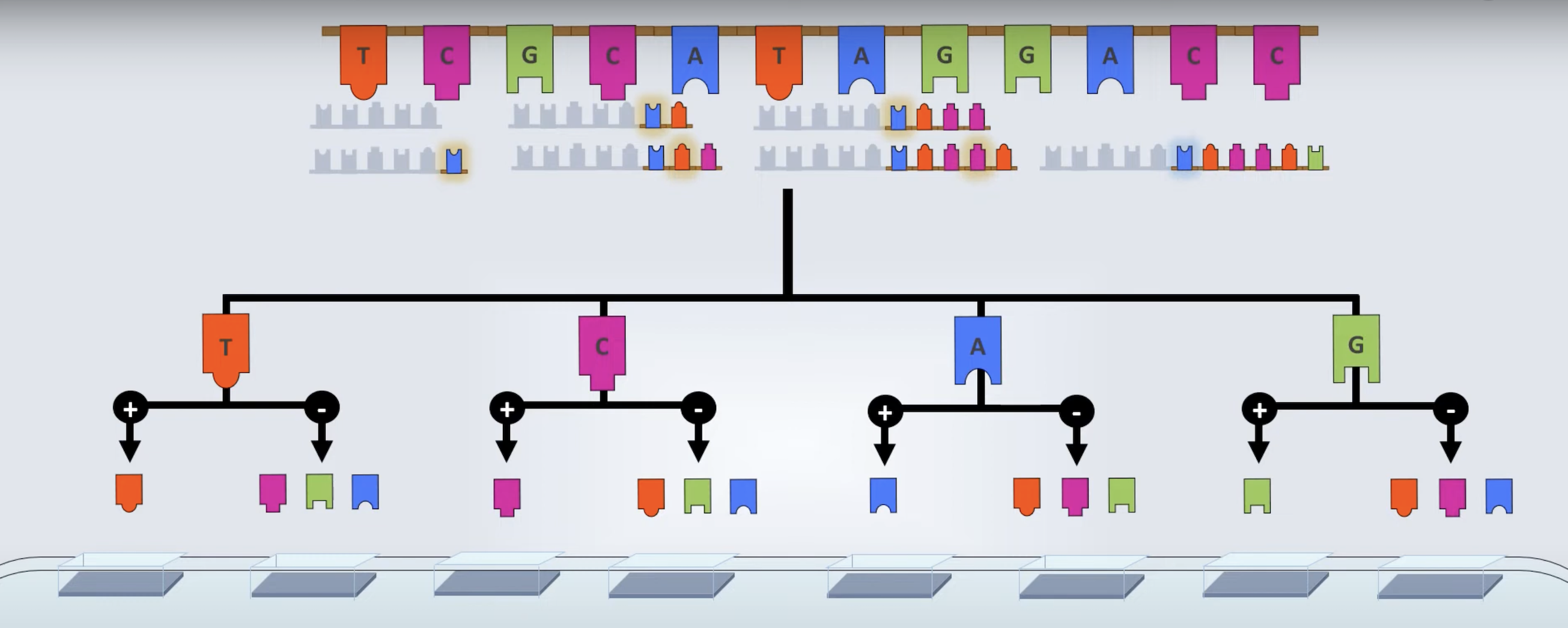
Polymerases can incorporate ddNTPs.
Leading to a single base extension followed by termination
No 3’hydroxyl group (3’OH).
“Sanger sequencing”
Radioactive 5’labeling
Chemical cleavage
PAGE
California. Genentech and recombinant technologies were already creating value. Flow cytometer and Beckman Coulter commercial machines.
⛰ Cal. Tech. 👥 Leroy Hood and Mike Hunkapiller 🏢 Applied Bioscience Inc. (ABI)
Fluorescently labeled nucleotides.
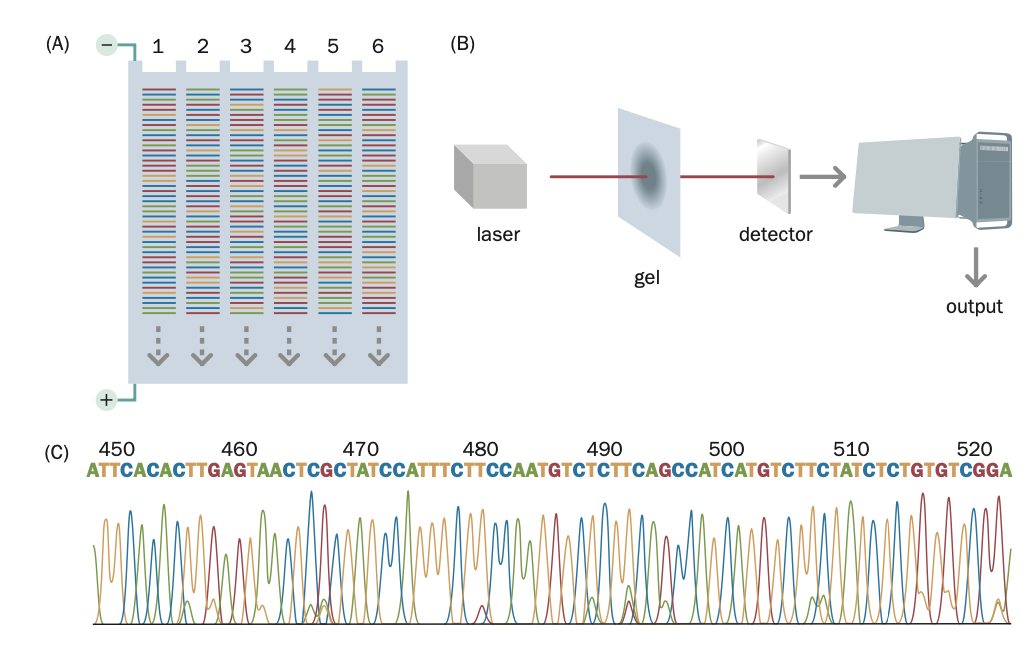
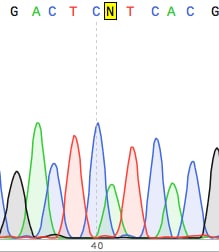
Base calling: assigning specific nucleotide bases to raw signals generated during sequencing.
Meetings that changed the world:
Santa Fe Workshop 1986.
All about how to massively multiplex sequencing.
Pyrosequencing
Sequencing by ligation
Reversible dye-terminators
Solid-phase substrate
Bridge amplification
Emulsion PCR
DNA nanoballs
Primer extension
Sequencing by synthesis
(SBS)
Sequencing by ligation
(SBL)
Principle: DNA polymerase incorporates nucleotides, releasing pyrophosphate (PPi).
Signal: PPi is converted to light via sulfurylase and luciferase, where the light intensity indicates the number of incorporated bases.
Analysis: Light signals are used to determine the DNA sequence in real time.
Question: How can individual bases (A, T, C, G) be discriminated?
patent 444 expired last year!)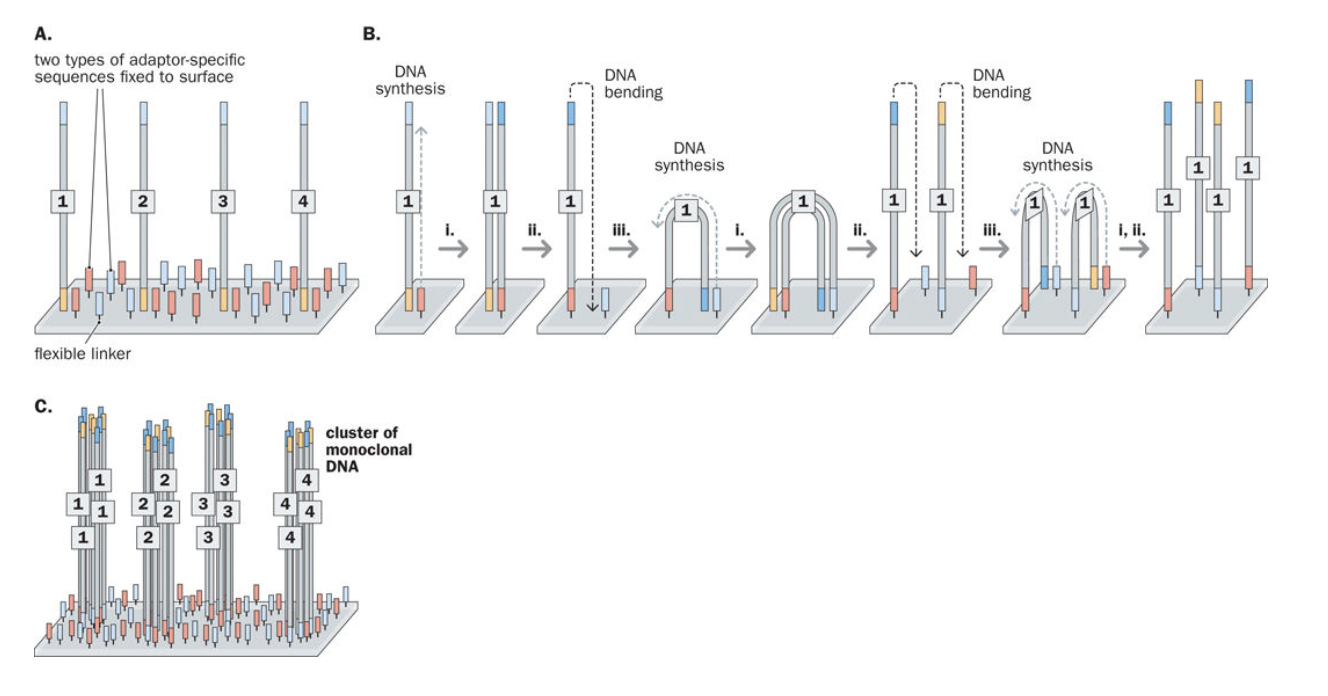
Bridge amplification
PCR used to flank our DNA library with P5 and P7 adapter sequence.
The library cannot be directly placed on the flow cell because it is double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and therefore cannot bind to the flow cell oligos.
The sequencing library is diluted to very low concentrations together with NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
NaOH is strongly basic, which denatures dsDNA into ssDNA.
The sequencing library is diluted to very low concentrations together with NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
NaOH is strongly basic, which denatures dsDNA into ssDNA.
The library is pumped onto the flow cell, and the pH is adjusted down, causing the ssDNA library to bind to the P5 and P7 oligos via hybridization.
Is actual DNA sequencing.
But the RNA is converted to cDNA by reverse transcriptase.
Alternative splicing
Intron retention, pre-mRNA
Alterative polyadenylation (3’UTR exon)
Strand-specificity

Tuesday 2nd Sept. Rudbecksalen, Rudbeck, 13:15 - 15:00